
Jeff Baldwin's youtube video - taking a LIT image
Jeff Baldwin's youtube video - processing a LIT image
click to download the 24 mega byte imageJ input tif file to be used with LIT spreadsheet
Olympus E300 Evolt
Canon T2i EOS Rebel
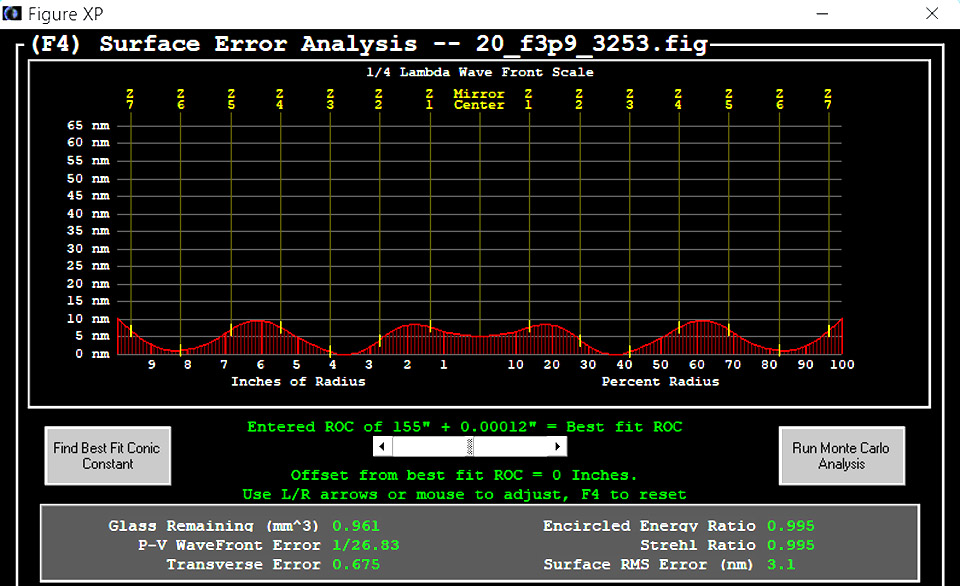
| Lateral Image Test | ||||
| Overview | Computations | Setup | ||
| Baldwin On LIT | Contact | |||

|
|
|
To download the LIT Conic spreadsheet click here (MD5 = DBD02BDD59DEF8F8BB2F8C260520543D) Jeff Baldwin's youtube video - taking a LIT image Jeff Baldwin's youtube video - processing a LIT image click to download the 24 mega byte imageJ input tif file to be used with LIT spreadsheet Olympus E300 Evolt Canon T2i EOS Rebel |
|
 |
|
| LIT Differential Equations Note: Click on equations 1, 2, 4, 5 and 7 to view intermediate steps |
||
|
This is a newer and I think easier to understand version of the LIT equations. The original equations can be found here. And of course, both produce the same results. LIT is a Fixed Source Test and as such, the angle of the source ray s is equal to the angle of reflection ray r as measured with respect to the Normal per Fig-1:
The Normal vector (per Fig-1 equation 2) of the form y=mx+b is y=-z'x+zz'+h, where zz'+h is the b term. Knowing z, the other side of that right triangle is found using similar triangles where the derivative z' serves as the other triangle with similar sides. Derivative z' and 1/z' are used in many places in Fig-1 in this manner which has greatly simplified this new version of the LIT equations, which gets exactly the same results as the old. Excels Solver (Root finder) is used to find the numerical solution to the LIT differential equations, which can be simply summarized as: z is varied (using a Root finder) until Yz of Fig-2 equation 12 is nearly equals to Ym (the slit images as measured by ImageJ). Instead of using Z=-Kz of Fig-4 to compute the Foucault, Z=(h-Rz'+zz')/z' is used instead being it avoids multiplying by K=-0 when the conic is a sphere. |

|

|

|

|
|
 |

|
|
 |
||
References
| ||||||
| Back to the top |
 2005 - 2026 Bill Thomas This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. |